A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell (PV cell), is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect. It is a form of photoelectric cell, a device whose electrical characteristics (such as current, voltage, or resistance) vary when it is exposed to light. Individual solar cell devices are often the electrical building blocks of photovoltaic modules, known colloquially as "solar panels". Almost all commercial PV cells consist of crystalline silicon, with a market share of 95%. Cadmium tellurium thin-film solar cells account for the remainder. The common single-junction silicon solar cell can produce a maximum open-circuit voltage of approximately 0.6 to 0.8 volts.
Photovoltaic cells may operate under sunlight or artificial light. In addition to producing energy, they can be used as a photo-detector (for example infrared detectors), detecting light or other electromagnetic radiation near the visible range, or measuring light intensity.
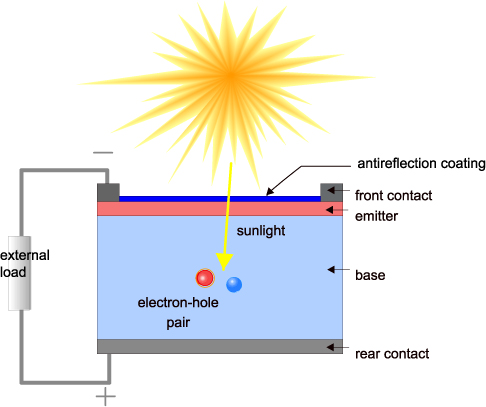
The operation of a PV cell requires three basic attributes:
The absorption of light, generating excitons (bound electron-hole pairs), unbound electron-hole pairs (via excitons), or plasmon.
The separation of charge carriers of opposite types.
The separate extraction of those carriers to an external circuit.
Multiple solar cells in an integrated group, all oriented in one plane, constitute a solar photovoltaic panel or module. Photovoltaic modules often have a sheet of glass on the sun-facing side, allowing light to pass while protecting the semiconductor wafers. Solar cells are usually connected in series creating additive voltage. Connecting cells in parallel yields a higher current.
However, problems in paralleled cells such as shadow effects can shut down the weaker (less illuminated) parallel string (a number of series connected cells) causing substantial power loss and possible damage because of the reverse bias applied to the shadowed cells by their illuminated partners.
Although modules can be interconnected to create an array with the desired peak DC voltage and loading current capacity, which can be done with or without using independent MPPTs (maximum power point trackers) or, specific to each module, with or without module level power electronic (MLPE) units such as micro-inverters or DC-DC optimizer. Shunt diodes can reduce shadowing power loss in arrays with series/parallel connected cells.

